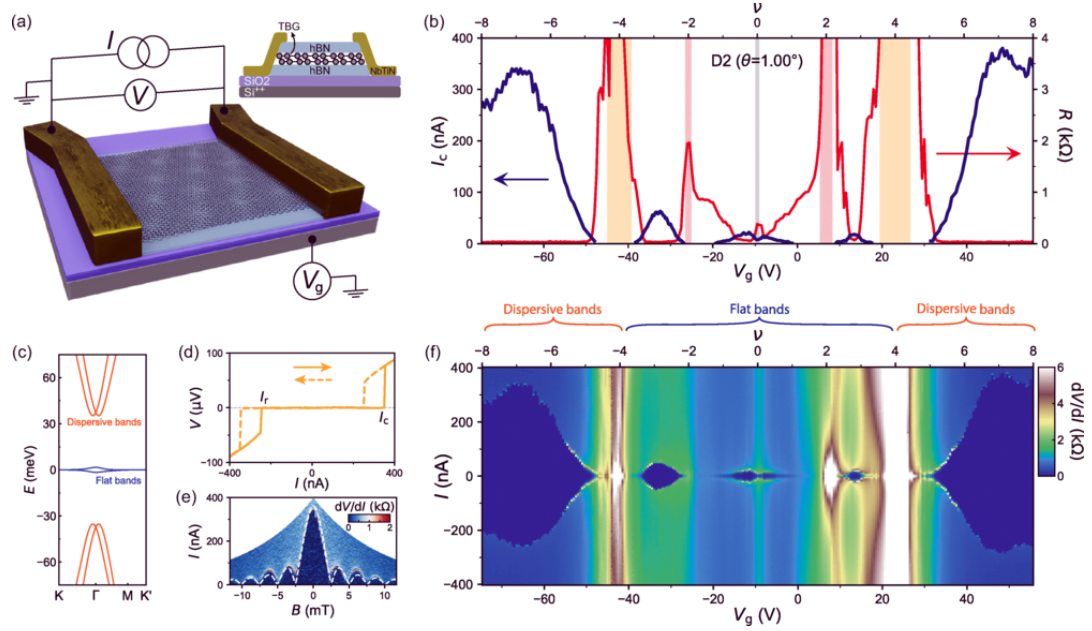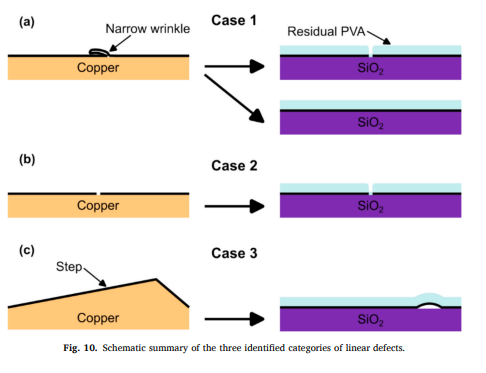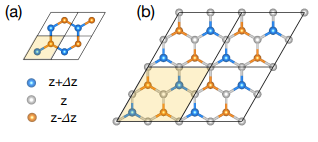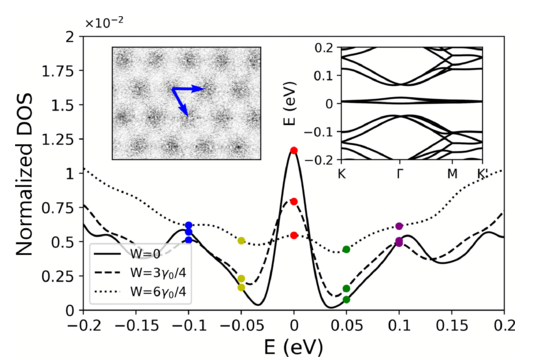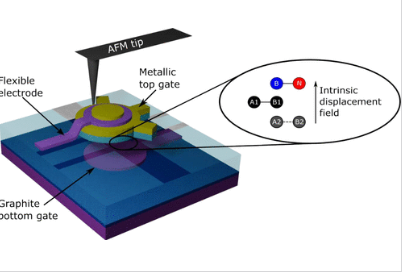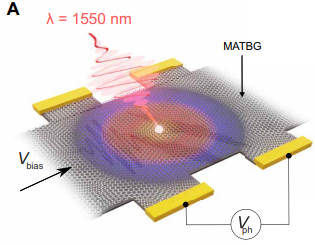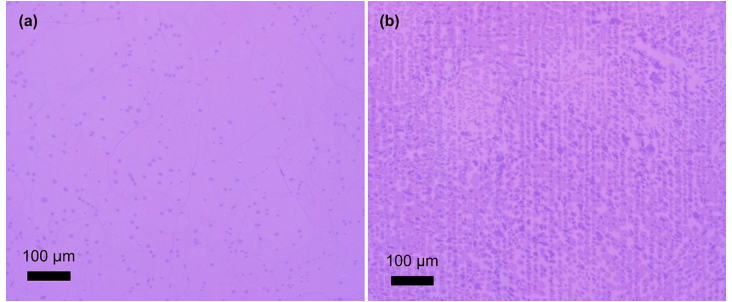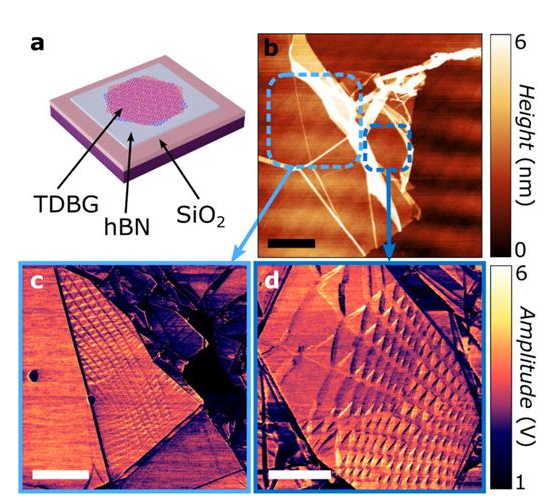
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have attracted significant interest due to their tunable physical properties when stacked into homo- and heterostructures. Twisting adjacent layers introduces moiré patterns that strongly influence the material’s electronic and thermal behavior. In twisted graphene systems, the twist...